As the name implies, rare-earth permanent magnet motors use rare-earth materials inside the motor. NdFeB rare-earth magnets are embedded in the rotor. The inherent magnetic field of the magnet is used as an excitation source to form a fixed magnetic pole. When the three-phase stator winding of the motor is fed with three-phase alternating current, a synchronous rotating magnetic field will be generated. According to the principle of magnetic pole homogeneity, repulsion and heterogeneous attraction, the stator rotating magnetic field drives the rotor magnetic pole to rotate, and finally reaches the rotor rotation speed equal to the stator magnetic field rotation speed. Therefore, rare earth permanent magnet motors are also called synchronous motors.
Rare-earth permanent magnet motors operate based on electromagnetic induction principles. The stator generates a rotating magnetic field when powered by AC current. This rotating field interacts with the constant magnetic field produced by rare-earth magnets embedded in the rotor. The interaction causes synchronous rotation of the rotor with no slip, meaning that both stator and rotor rotate at the same frequency.
The rotor is excited by permanent magnets, and no reactive excitation current is needed. Therefore, the power factor is improved, the reactive power is reduced, the stator current is greatly reduced, and the stator copper and iron losses are greatly reduced.
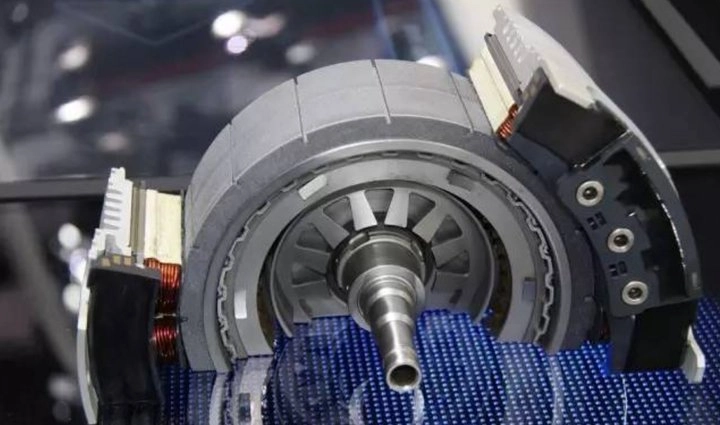

The stator consists of laminated steel cores and windings that produce a rotating magnetic field. The rotor includes embedded rare-earth magnets that follow this rotating field synchronously.
NdFeB rare-earth magnets are embedded in the rotor. These magnets serve as a constant excitation source without requiring additional electrical energy input. Their high coercivity ensures strong magnetization even under demanding operational conditions.
NdFeB magnets are widely used due to their high energy density and strong magnetic properties. They offer excellent performance in compact designs but are sensitive to high temperatures.
Cooling systems vary from air cooling to water cooling depending on application demands. Proper housing ensures mechanical protection and environmental sealing for long-term reliability.
Motor efficiency is equal to IE4 (High efficiency: above GB1 level). Compared with asynchronous motor, it may reduce current capacity of equipment due to high power factor.
Volume average 35% smaller, weight average 40% lighter. Motor frame No. is decreased by 1-3 compared with asynchronous motor. It can realize mechanical miniaturization to save space.
SmCo variants enable stable operation at elevated temperatures without demagnetization risks common with NdFeB in extreme heat environments.
The efficiency curve of the rare earth permanent magnet motor is high and flat, and it is in the high efficiency area at 20%~120% of the rated load.
Due to their compact size and powerful magnets, these motors deliver higher torque per unit weight than conventional motors.
Direct drive type eliminates reducer transmission; running noise is greatly reduced and installed area is saved. It keeps high efficiency output in wide load range (motor efficiency usually stays above 0.95), which makes it almost maintenance-free.
Rare earth permanent magnet synchronous motors have higher out-of-step torque and pull-in torque, which makes the motor have higher load capacity and can be smoothly pulled into synchronization.
Compared with the asynchronous motor of the same specificationthe price of rare earth magnetic steel material is high; therefore, the motor manufacturing cost is high, which is common for asynchronous motors about 2 times.
When the permanent magnet material is subjected to vibration, high temperature and overload currentdemagnetization phenomenon occurs, which reduces performance of permanent magnet motor.
Mining processes for rare earth elements raise environmental issues such as habitat destruction, water contamination, and geopolitical supply chain dependencies.
Improper handling or exposure to excessive heat or currents can lead to irreversible demagnetization affecting long-term reliability.
Q: Can a rare-earth permanent magnet motor replace an asynchronous motor directly?
A: Due to same frame No. design with asynchronous motor (output <315 kW), installation size is same which can be changed easily.
Q: What voltage levels do these motors support?
A: Voltage grades include 380V, 690V, 1140V up to 10kV depending on application requirements.
Q: Are these motors suitable for low-speed applications?
A: Low speed direct drive high torque permanent magnet motor has motor efficiency above IE4 grade; it eliminates reducer transmission making it ideal for belt machines or mixers.
Q: Do they require special controllers?
A: Except that low speed direct drive motor must be equipped with this inverter; other products are optional with EN series frequency converters designed specifically for synchronous drives.
Qingdao Enneng Motor Co., Ltd offers industry-specific solutions using PM motor technology tailored for sectors like petrochemical, mining, rubber tire manufacturing, ports, water conservation systems among others. We always adhere to corporate principle of integrityto provide customers with stable and reliable permanent magnet motor technology solutions aligned with our mission to save energy and conserve environment. Their product line includes standard TYB series for compact needs, TYP general series matching traditional frame sizes for easy retrofitting, TYPCX special models customized per industry demand including ENM models dedicated for tire manufacturing machinery.
For large-scale industrial upgrades or energy-saving retrofits—ENNENG’s cutting-edge rare-earth permanent magnet motors deliver unmatched performance across all load ranges while minimizing operational costs through superior efficiency. Contact ENNENG today for rare-earth permanent magnet motors ordering.