Two main technologies stand out in the field: permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) and induction motors (AICMs).
Permanent magnet motors (PMSMs) use strong magnets, like neodymium or samarium-cobalt, placed in the rotor to create a steady magnetic field. This removes the need for outside electrical power, cutting energy waste and boosting efficiency. These motors are widely used in HVAC compressors, and machines like direct-drive washing machines. For example, ENNENG’s TYB series motors use top-quality NdFeB magnets and meet IE4+ efficiency standards. They save 5-10% more energy compared to older designs. Their rotor design skips windings. This makes upkeep easier and improves dependability in tough places like mining and oil fields.

Induction motors (AICMs) depend on electromagnetic induction to create current in the rotor. When alternating current (AC) flows through the stator windings, it forms a spinning magnetic field. This field causes currents in the rotor’s copper or aluminum conductors. The interaction makes torque, but it has energy losses due to “slip.” Slip is the speed gap between the rotor and the magnetic field. Induction motors are often used in pumps, fans, and older factory systems.
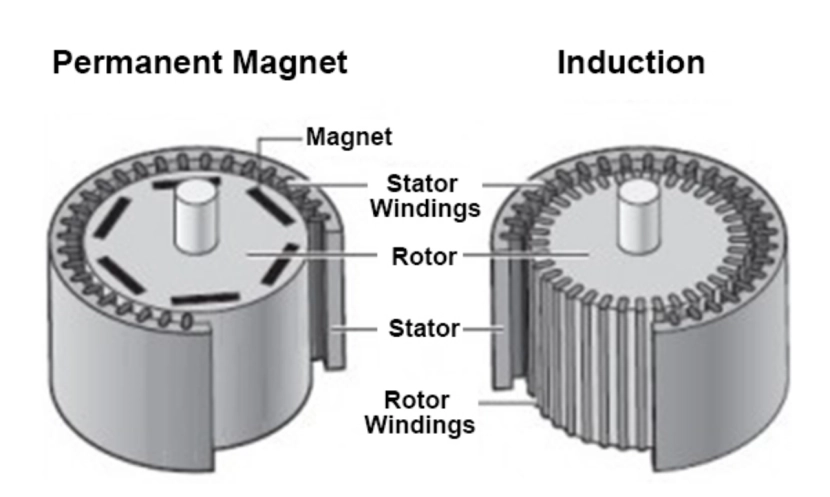
PMSM: The rotor has permanent magnets, so it doesn’t need windings or slip rings. ENNENG’s TYDP series, for example, uses a direct-drive design. This simplifies parts and reduces wear. The lack of rotor windings also lowers heat, making PMSMs great for precise tasks like robotics and textile machines.
Induction Motors: The rotor has conductive bars (squirrel-cage design) or wound coils. It needs slip to create torque. This adds mechanical complexity and upkeep needs, especially in fast tasks like conveyor systems.
PMSM: With no rotor current losses, PMSMs are 5-10% more efficient. ENNENG’s IE4+ motors cut grid losses by up to 25%. They are perfect for energy-heavy industries like mining and water treatment. For instance, a 1500W PMSM can reach 80% efficiency with variable frequency control. It performs much better than induction motors in partial-load situations.
Induction Motors: Rotor currents cause 3-4% energy loss, especially at partial loads. Their efficiency drops a lot in low-speed tasks. They often need extra parts like variable frequency drives (VFDs) to work better.
PMSM: Offers exact torque control, even at low speeds. ENNENG’s FTYP series for textile machines ensures steady work in variable-speed settings. It has a frequency range of 2-75Hz and torque accuracy within ±1%. This makes PMSMs good for tasks needing quick responses, like power steering and CNC machines.
Induction Motors: They have limited torque at low speeds. They need complex inverters for speed changes, which raises costs. They work well in fast tasks like fans. But their response is slower than PMSMs in precise tasks.
PMSM: They cost more at first due to rare-earth magnets. But they have lower long-term costs. ENNENG’s motors, for example, cut downtime by 30% in oil field tasks through strong design and less wear. Their modular build allows easy replacement of parts like bearings. This extends service times.
Induction Motors: They have lower starting costs. But they have higher energy and upkeep bills over time. For example, a 10kW induction motor may use 15-20% more electricity each year compared to a PMSM.
PMSMs shine in high-efficiency tasks:
Induction motors do well in cost-focused, high-speed tasks:
ENNENG provides tailored motors for industries like mining and rubber production. Their coal mine projects saved 15% energy using direct-drive TYDP series motors. Oil field setups cut downtime by 40% through careful engineering. Customization options include:
PMSMs provide better efficiency (up to 95% in IE4+ models), precise control, and lower long-term costs. Their small design also saves 20-30% installation space compared to induction motors.
Check the rotor. PMSMs have visible magnets. Induction motors use conductive bars or coils. Or measure no-load efficiency. PMSMs usually keep >90% efficiency even at 25% load.
Transform your operations with motors built for top performance. At ENNENG, we combine innovation with real-world expertise to deliver great efficiency. Contact us at sales@enpmsm.com for a free consultation. Or explore our case studies on PMSM-driven breakthroughs in energy-heavy industries.